Preparing for the CCNA exams
When studying for these exams, it’s best to prepare the way that works for you. For those who have some experience with networking, self-study is a popular option, and you can do so using any number of available resources, including the courses available through Pluralsight. In my experience, self-study works well when coupled with considerable practice on Cisco’s IOS. For most people at the CCNA level, using a product like GNS3 combined with computer-based training is an excellent approach. For the CCNA R&S exams, make sure you understand the fundamentals, IP subnetting, addressing and basic routing, before looking at other topics. Regardless of the changes to these exams, the fundamentals will always be covered.
For most of the tests that Cisco offers, cramming isn’t a useful option and should be avoided. Go through all of the topics in IOS and learn them, configure them and figure out how and why they work. Cisco IOS is generally a well-documented OS. Cisco also has a very active certification support community that can provide specific advice as issues arise.
Preparing for any test can be stressful, and Cisco’s CCNAs are no exception. No matter how much studying you’ve done, it won’t be of much use if you’re tired or distracted. The best thing you can do to prepare is to get plenty of sleep, and go into your exams as relaxed and confident as possible.
1
Fill in the blank. Do not use abbreviations.
A network engineer is troubleshooting the configuration of new VLANs on a
network. Which command is used to display the list of VLANs that
exists on the switch? ”
show vlan ”
2
What is a disadvantage of using multilayer switches for inter-VLAN routing?
Multilayer switches have higher latency for Layer 3 routing.
Spanning tree must be disabled in order to implement routing on a
multilayer switch.
Multilayer switches are more expensive than router-on-a-stick implementations.*
Multilayer switches are limited to using trunk links for Layer 3 routing.
3
 Refer to the exhibit. A router-on-a-stick configuration was
implemented for VLANs 15, 30, and 45, according to the show
running-config command output. PCs on VLAN 45 that are using the
172.16.45.0 /24 network are having trouble connecting to PCs on VLAN 30
in the 172.16.30.0 /24 network. Which error is most likely causing this
problem?
Refer to the exhibit. A router-on-a-stick configuration was
implemented for VLANs 15, 30, and 45, according to the show
running-config command output. PCs on VLAN 45 that are using the
172.16.45.0 /24 network are having trouble connecting to PCs on VLAN 30
in the 172.16.30.0 /24 network. Which error is most likely causing this
problem?
The command no shutdown is missing on GigabitEthernet 0/0.30
The GigabitEthernet 0/0
interface is missing an IP address.
There is an incorrect IP address configured on GigabitEthernet 0/0.30.*
The wrong VLAN has been configured on GigabitEthernet 0/0.45
4
 Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator
has configured router CiscoVille with the above commands to provide
inter-VLAN routing. What command will be required on a switch that is
connected to the Gi0/0 interface on router CiscoVille to allow
inter-VLAN routing?
switchport mode trunk*
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator
has configured router CiscoVille with the above commands to provide
inter-VLAN routing. What command will be required on a switch that is
connected to the Gi0/0 interface on router CiscoVille to allow
inter-VLAN routing?
switchport mode trunk*
switchport mode dynamic desirable
switchport mode access
no switchport
5
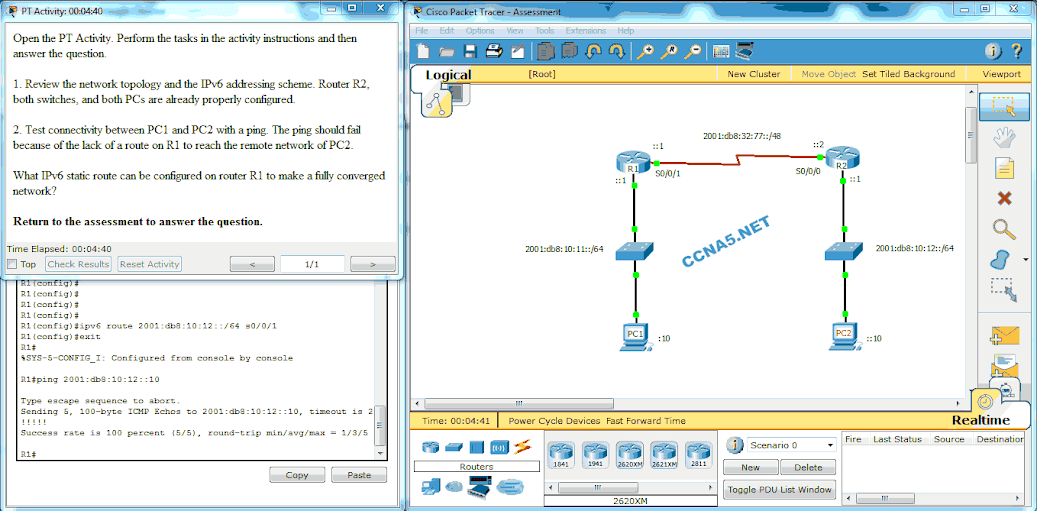
 Refer to the exhibit. The switch does the routing for the hosts that connect to VLAN 5. If the PC accesses a web server from the Internet, at what point will a VLAN number be added to the frame?
Refer to the exhibit. The switch does the routing for the hosts that connect to VLAN 5. If the PC accesses a web server from the Internet, at what point will a VLAN number be added to the frame?
point A
point B
point D
point C
point E
No VLAN number is added to the frame in this design.*
6
Inter-VLAN communication is not occurring in a particular
building of a school. Which two commands could the network administrator
use to verify that inter-VLAN communication was working properly
between a router and a Layer 2 switch when the router-on-a-stick design method is implemented? (Choose two.)
From the switch, issue the show vlans command.
From the router, issue the show interface interface command.
From the switch, issue the show interface trunk command.*
From the switch, issue the show interface interface command.
From the router, issue the show ip route command.*
From the router, issue the show interface trunk command.
7
 Refer to the exhibit. Router RA receives a packet with a source
address of 192.168.1.35 and a destination address of 192.168.1.85. What
will the router do with this packet?
Refer to the exhibit. Router RA receives a packet with a source
address of 192.168.1.35 and a destination address of 192.168.1.85. What
will the router do with this packet?
The router will drop the packet.
The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.2 and interface FastEthernet 0/1.3.
The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.1.
The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.2.*
The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.3.
8
What condition is required to enable Layer 3 switching?
All participating switches must have unique VLAN numbers.
Inter-VLAN portions of Layer 3 switching must use router-on-a-stick.
The Layer 3 switch must have IP routing enabled.*
All routed subnets must be on the same VLAN.
9
Which type of inter-VLAN communication design requires the configuration of multiple subinterfaces?
legacy inter-VLAN routing
routing for the
management VLAN
router on a stick*
routing via a multilayer switch
10
 Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring RT1
for inter-VLAN routing. The switch is configured correctly and is
functional. Host1, Host2, and Host3 cannot communicate with each other.
Based on the router configuration, what is causing the problem?
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring RT1
for inter-VLAN routing. The switch is configured correctly and is
functional. Host1, Host2, and Host3 cannot communicate with each other.
Based on the router configuration, what is causing the problem?
Routers do not support 802.1Q encapsulation on subinterfaces.
IP addresses on the subinterfaces are incorrectly matched to the VLANs.*
Each subinterface of Fa0/0 needs separate no shutdown commands.
Interface Fa0/0 is missing IP address configuration information.
11
How is traffic routed between multiple VLANs on a multilayer switch?
Traffic is routed via internal VLAN interfaces.*
Traffic is routed via physical interfaces.
Traffic is broadcast out all physical interfaces.
Traffic is routed via subinterfaces.
12
 Refer to the exhibit. Communication between the VLANs is not occurring. What could be the issue?
Refer to the exhibit. Communication between the VLANs is not occurring. What could be the issue?
The wrong port on the router has been used.
The Gi1/1 switch port is not in trunking mode.*
Default gateways have not been configured for each VLAN.
A duplex issue exists between the switch and the router.
13
What is a disadvantage of using router-on-a-stick inter-VLAN routing?
does not support VLAN-tagged packets
does not scale well beyond 50 VLANs*
requires the use of multiple router interfaces configured to operate as access links
requires the use of more physical interfaces than legacy inter-VLAN routing
14
Which statement describes a disadvantage of using router subinterfaces for inter-VLAN routing?
Routed traffic must contend for bandwidth on a single router interface.*
All untagged traffic is dropped.
It is more expensive than using individual router interfaces.
Trunking cannot be used to connect the router to the switch.
15
Fill in the blank with an acronym.
While configuring inter-VLAN routing on a multilayer switch, a/an ”
SVI ” is used as a virtual-routed VLAN interface.
16
 Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is verifying the
configuration of inter-VLAN routing. Users complain that PC2 cannot
communicate with PC1. Based on the output, what is the possible cause of
the problem?
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is verifying the
configuration of inter-VLAN routing. Users complain that PC2 cannot
communicate with PC1. Based on the output, what is the possible cause of
the problem?
The command interface GigabitEthernet0/0.5 was entered incorrectly.
There is no IP address configured on the interface Gi0/0.
The encapsulation dot1Q 5 command contains the wrong VLAN.*
The no shutdown command is not entered on subinterfaces.
Gi0/0 is not configured as a trunk port.
17
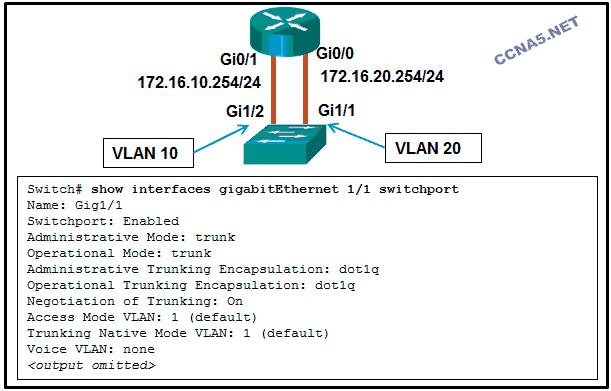 Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is verifying the
configuration of inter-VLAN routing. Users complain that PCs on
different VLANs cannot communicate. Based on the output, what are two
configuration errors on switch interface Gi1/1? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is verifying the
configuration of inter-VLAN routing. Users complain that PCs on
different VLANs cannot communicate. Based on the output, what are two
configuration errors on switch interface Gi1/1? (Choose two.)
The trunking encapsulation protocol is configured wrong.
Negotiation of trunking is turned on on Gi1/1.
Gi1/1 is configured as trunk mode.*
Voice VLAN is not assigned to Gi1/1.
Gi1/1 is in the default VLAN.*
18
While configuring inter-VLAN routing on a multilayer switch, a
network administrator issues the no switchport command on an interface
that is connected to another switch. What is the purpose of this
command?
to create a switched virtual interface
to provide an access link that tags VLAN traffic
to create a routed port for a single network*
to provide a static trunk link
19
The PT initialization was skipped. You will not be able to view the PT activity.
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Fill in the blank. Do not use abbreviations.
Which command is missing on the Layer 3 switch to restore the full connectivity between PC1 and the web server?
“
ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 ”
20
A small college uses VLAN 10 for the classroom network and VLAN
20 for the office network. What is needed to enable communication
between these two VLANs while using legacy inter-VLAN routing?
A switch with a port that is configured as trunk is needed to connect to a router.
Two groups of switches are needed, each with ports that are configured for one VLAN.
A router with at least two LAN interfaces should be used.*
A router with one VLAN interface is needed to connect to the SVI on a switch.
21
 Refer to the exhibit. After attempting to enter the
configuration that is shown in router RTA, an administrator receives an
error and users on VLAN 20 report that they are unable to reach users on
VLAN 30. What is causing the problem?
Refer to the exhibit. After attempting to enter the
configuration that is shown in router RTA, an administrator receives an
error and users on VLAN 20 report that they are unable to reach users on
VLAN 30. What is causing the problem?
The no shutdown command should have been issued on Fa0/0.20 and Fa0/0.30.
There is no address on Fa0/0 to use as a default gateway.
Dot1q does not support subinterfaces.
RTA is using the same subnet for VLAN 20 and VLAN 30.*
22
 Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to configure
router-on-a-stick for the networks that are shown. How many
subinterfaces will have to be created on the router if each VLAN that is
shown is to be routed and each VLAN has its own subinterface?
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to configure
router-on-a-stick for the networks that are shown. How many
subinterfaces will have to be created on the router if each VLAN that is
shown is to be routed and each VLAN has its own subinterface?
5
3
1
4*
2
23
 Refer to the exhibit. Which command can the administrator issue to change the VLAN10 status to up?
Switch1(config)# vlan 10*
Refer to the exhibit. Which command can the administrator issue to change the VLAN10 status to up?
Switch1(config)# vlan 10*
Switch1(config)# interface vlan 10
Switch1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Switch1(config)# interface vlan 10
Switch1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Switch1(config-if)# no shutdown
Switch1(config)# interface vlan 10
Switch1(config-if)# no shutdown
Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Routing and Switching is a certification program for entry-level network engineers that helps maximize your investment in foundational networking knowledge and increase the value of your employer's network. CCNA Routing and Switching is for Network Specialists, Network Administrators, and Network Support Engineers with 1-3 years of experience. The CCNA Routing and Switching validates the ability to install, configure, operate, and troubleshoot medium-size routed and switched networks